DNA-The Next Gen Archival Storage
Everyday 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are produced all over the world. That is almost equal to 2500000000 Gbs of raw data. Quite a large number right? But this number is not stagnant. It is rapidly increasing day by day as we are developing more and more IoT systems. Soon this number is going to be so huge that traditional storage devices will seem to be very tiny. In that case we need a storage component whose storage density must be too high that we can fit millions and millions of GBs of data into a very tiny space. Here comes DNA to solve that problem.
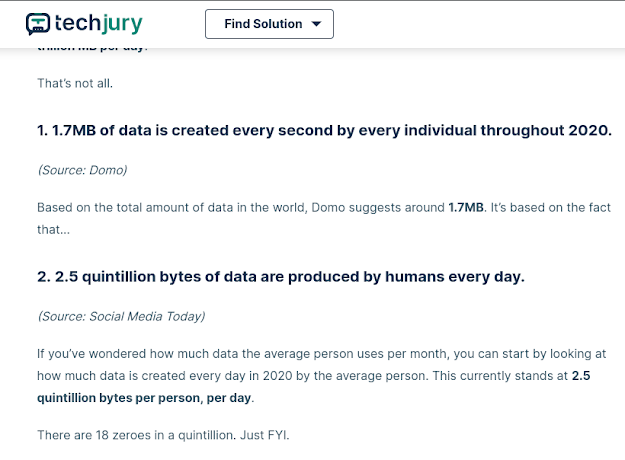 |
| Screen Shot From techjury.net |
Deoxyribonucliec acid or simply DNA is the building block of any living organism. You may know that DNA has a double helix model which is nothing but a twisted ladder like structure consisting of 4 components named Adenine(A), Guanine(G), Thymine(T) & Cytosine(C). The two strands of DNA is called polynucleotides. These two polynucleotides are attached together with huge number of bondings containing either A-T or G-C combination. This sequence of A-T or G-C contains the genetic information which is inherited from previous generation to present generation. A single human polynucleotide contains 770 Mbs of data in males and 756 Mbs of data in females. That means a full human DNA structure contains almost 1512-1540 Mb data(some people say it is almost double in size if not compressed).
DNA or better to say human genome can contain a very large amount of data. Scientists say a single gram of DNA can contain 215 petabytes of data which is equals to 215000000 Gbs, that implies you can store approximately 209961 movies worth 1 Gb of size! Isn’t that amazing!! We can’t even imagine that our body is a living data-centre which has the capability of storing all the data scattered all over the world.
Scientists are developing a process called “DNA digital data storage” which encodes data in binary format to synthetic strand of DNA and vice versa. In this process the DNA bases are represented in 2 bit binary format such as A=00, C=01, G=10 & T=11. This makes easy to encode the binary data in A-G-T-C base pair sequence. Using this process, in June 2019, 16 Gb of text data from Wikipedia was encoded into synthetic DNA.
 |
Screen Shot From Wikipedia |
DNA is not only giving us a storage solution but also shaping new technologies. A concept technology has started evolving around this process named “DNA of Things”. DNA of Things or DoT encodes digital data into DNA modules which are then embedded into objects. Unlike Internet of Things in which the computing devices are interrelated and uses the same shared storage, DoT creates independent storage objects connected to each other. This will ensure better connectivity and performance of the connected computing devices.
DNA data storage technology has the potential to replace the traditional hard drive and tape drive storage devices used in the data centers. This technology will reduce the size of the storage devices significantly. This proves not humans but nature has the best technologies. There are many mysteries hidden underneath the foggy layers of nature which is totally unknown to us, but as human technology is advancing we are witnessing the carismatic creations of nature which leaves us surprised. May be humans need another thousand year to develop such marvelous technology which nature created millions and millions of years ago...
For a better view check out this youtube video from "TED-ED":


Comments
Post a Comment